This article provides 20 practical tips and strategies for managing anxiety in individuals with autism, including the importance of early intervention, self-care practices, coaching, and creating a supportive environment.
Introduction to Managing Anxiety in Autism
Anxiety in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) refers to feelings of worry, fear, or unease that can significantly impact their daily lives. It is essential to understand that anxiety is not part of the diagnostic criteria for autism, yet many individuals with autism experience it. Unmanaged anxiety can have a profound effect on the quality of life for individuals with autism, affecting their interactions, well-being, and overall functioning.
Recognising these challenges, it is crucial to delve deeper into the prevalence of anxiety among individuals with autism. Research indicates that anxiety is a common comorbidity in autistic individuals, with estimates suggesting that up to 40% of children and adolescents with autism also experience clinically significant anxiety. This high prevalence underscores the necessity of addressing anxiety in the autism community to enhance the overall quality of life for these individuals.
Moreover, the impact of unmanaged anxiety on individuals with autism can manifest in various ways. For instance, anxiety can heighten sensory sensitivities, leading to increased distress and potential meltdowns in response to overwhelming stimuli. Additionally, anxiety may exacerbate social challenges, making it difficult for individuals with autism to navigate social interactions and form meaningful connections. By understanding these facets of anxiety in autism, interventions and support systems can be tailored effectively to address the unique needs of individuals on the spectrum.
Understanding Anxiety in Autism
Common anxiety triggers for individuals with autism encompass a range of factors, from disruptions to routines and sensory sensitivities to challenges in social interactions. For instance, a sudden change in routine, like an unexpected transition from one activity to another, can trigger anxiety in autistic individuals. Moreover, sensory sensitivities, such as sensitivity to loud noises or bright lights, can overwhelm their senses and lead to heightened anxiety levels. These triggers highlight the importance of creating structured and predictable environments to help individuals with autism feel secure and reduce anxiety-provoking situations.
In addition to disruptions in routines and sensory sensitivities, challenges in social interactions can significantly contribute to anxiety among individuals with autism. For example, difficulties in interpreting social cues or engaging in reciprocal conversations can lead to feelings of isolation and anxiety. This social anxiety can be exacerbated in unfamiliar or overwhelming social settings, making it essential to provide support and tools to help autistic individuals navigate social scenarios effectively. By recognising these common triggers and understanding their impact, caregivers and professionals can tailor interventions to alleviate anxiety and promote a better quality of life for individuals with autism.

Practical Tips for Managing Anxiety in Autism
Autism coaches are invaluable in assisting individuals with autism in managing anxiety, offering tailored strategies and ongoing support to navigate the challenges they face. For example, an autism coach may work with an individual to create a personalised anxiety management plan that includes identifying triggers, implementing coping mechanisms, and setting achievable goals to reduce anxiety levels effectively.
In addition to the support provided by autism coaches, self-care practices are essential tools for individuals with autism to incorporate into their daily lives to manage anxiety symptoms. For instance, practising mindfulness techniques enables individuals to stay present in the moment, reducing overthinking and promoting a sense of calm. Furthermore, deep breathing exercises can help regulate emotions during moments of heightened anxiety, providing a practical and accessible way to cope with stress. Moreover, taking sensory breaks, such as stepping away from overwhelming environments or engaging in soothing activities, can offer individuals with autism the opportunity to recharge and reset, contributing to improved emotional well-being and anxiety management.
Moreover, integrating relaxation techniques and stress-reduction activities into daily routines can be transformative for individuals with autism in managing anxiety [4]. For example, engaging in activities like yoga, meditation, or listening to calming music can help regulate emotions and promote relaxation, offering individuals effective tools to cope with anxiety triggers. By establishing these practices as part of their daily routines, individuals with autism can proactively address their anxiety symptoms, enhance their emotional resilience, and improve their overall well-being [4].
Creating a Supportive Environment for Individuals with Autism
Creating a supportive environment for individuals with autism involves implementing various strategies to ensure their well-being and comfort. For instance, using visual schedules and social stories can help individuals with autism understand expectations and reduce anxiety by providing predictability in their routines. By establishing routines and incorporating visual aids, caregivers and educators can offer individuals with autism a sense of structure and stability, which can significantly decrease feelings of uncertainty and anxiety. Additionally, deep pressure stimulation and proprioception techniques, such as weighted blankets or compression garments, can help calm individuals with autism by providing sensory input that aids in regulating their nervous systems and promoting relaxation.
Moreover, when designing sensory-friendly environments, it is essential to consider the individual sensory sensitivities of each person with autism. For example, creating quiet spaces with dimmed lighting and noise-canceling headphones can be beneficial for those who are sensitive to loud noises and bright lights. By being mindful of sensory triggers and adapting the environment accordingly, caregivers and educators can foster a safe and comfortable space where individuals with autism feel secure and supported. Ultimately, by tailoring the environment to accommodate the specific needs of individuals with autism, it becomes possible to minimise anxiety triggers and create a setting that promotes their overall well-being and mental health.

Autism Coaching for Anxiety
Collaboration with autism coach plays a crucial role in supporting individuals with autism in managing anxiety effectively. These coaches work together with the client to create personalised anxiety management strategies that are tailored to the unique strengths, needs and challenges of each individual. For example, an autism coach may help an individual with autism identify specific anxiety triggers, develop coping mechanisms, and establish a structured routine to promote a sense of security and predictability in their daily life.
Moreover, gradual exposure therapies, such as systematic desensitisation, are often utilised to help individuals with autism gradually confront and overcome their fears or anxieties. This approach involves exposing the individual to anxiety-provoking situations or stimuli in a controlled and gradual manner, allowing them to build resilience and develop effective coping strategies over time. Similarly, social stories, which are short narratives that describe social situations and appropriate responses, can assist individuals with autism in understanding and navigating challenging social interactions that may trigger anxiety.
Strategies for Anxiety Management in Autism
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) has been widely acknowledged for its effectiveness in reducing anxiety symptoms in individuals with autism. By focusing on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and behaviours, CBT equips individuals with valuable skills to manage their anxiety. For instance, a person with autism who experiences social anxiety in group settings may benefit from CBT sessions that help them reframe their thoughts about social interactions and develop coping mechanisms to navigate such situations more comfortably. In cases where anxiety symptoms are severe and significantly impact an individual’s daily functioning, healthcare professionals may consider the use of medications as part of the treatment plan.
Moreover, it is crucial to recognise the importance of tailoring anxiety management strategies to the specific neurology and requirements of each individual with autism. What works effectively for one person may not be as beneficial for another, highlighting the necessity for personalised support and interventions. By customising anxiety management approaches, such as coaching and incorporating sensory-based relaxation techniques, for those with sensory sensitivities, individuals with autism can receive the tailored support they need to effectively manage their anxiety.
Discover effective strategies and practical tips for managing anxiety and ADHD symptoms, including tools for organisation, coping strategies for daily life, and self-help techniques for individuals with ADHD and anxiety.
Overview of Anxiety Management in Individuals with ADHD
Anxiety is highly prevalent in individuals with ADHD, affecting around 50% of adults. Addressing anxiety symptoms is crucial for enhancing overall quality of life and daily functioning. Anxiety can significantly impact individuals with ADHD, exacerbating ADHD symptoms such as time blindness and emotional dysregulation. For example, individuals with ADHD may struggle with managing their time effectively and regulating their emotions when anxiety levels are high.
Moreover, the relationship between ADHD and anxiety is complex, with ADHD often intensifying anxiety symptoms due to challenges like poor working memory and impulsivity. This interconnection can lead to a cycle where anxiety worsens ADHD symptoms, creating a challenging environment for individuals. To manage this, individuals may benefit from cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) to address both core ADHD symptoms and anxiety-related issues. CBT can help individuals recognise and reframe negative thought patterns, providing them with practical tools to navigate through anxious moments.
Understanding the Relationship Between ADHD and Anxiety
The relationship between ADHD and anxiety is complex and often intertwined, as individuals with ADHD have a higher likelihood of experiencing anxiety disorders. This increased susceptibility is due to the unique challenges posed by ADHD, including issues like poor working memory and impulsivity, which can exacerbate anxiety symptoms. For example, the tendency to become overwhelmed by tasks and stimuli due to ADHD symptoms can trigger anxiety in various situations. Moreover, the constant struggle to maintain focus and complete tasks can fuel feelings of anxiety and stress in individuals with ADHD.
Moreover, the comorbidity of anxiety with adult ADHD underscores the importance of adopting holistic treatment strategies that address both conditions simultaneously. Integrated approaches that consider the interconnected nature of ADHD and anxiety can lead to more effective outcomes in managing symptoms and improving overall well-being. By recognising how ADHD symptoms can contribute to heightened anxiety levels, individuals can work towards developing coping mechanisms that target the root causes of their distress, ultimately enhancing their quality of life and daily functioning.

Practical Tips for Managing Anxiety and ADHD Symptoms
When it comes to managing anxiety and ADHD symptoms, practical tips play a crucial role in enhancing daily functioning. Utilising tools like wall calendars, colour-coding systems, and smartphone apps can significantly aid individuals in better organising their tasks and improving memory retention [1]. For instance, colour-coding different activities can help individuals with ADHD visualise their schedule more effectively and reduce feelings of being overwhelmed by a chaotic routine.
Additionally, breaking down tasks into smaller, manageable deadlines and incorporating time management techniques such as the Pomodoro Technique can assist individuals in staying on track and minimising anxiety levels. By dividing tasks into smaller steps and allocating specific time frames for each activity, individuals can prevent procrastination and improve their productivity. This structured approach not only helps in managing ADHD symptoms but also reduces the likelihood of feeling anxious due to looming deadlines and unfinished tasks. Moreover, implementing strategies to combat unhelpful thought patterns through techniques like reframing and creating designated areas for urgent tasks can empower individuals to maintain a sense of control over their responsibilities and minimise anxiety. For example, practising positive self-talk and designating a specific workspace for urgent tasks can prevent distractions and enhance focus, consequently reducing anxiety levels in individuals dealing with ADHD.
Coping Strategies for Daily Life
In addition to regulating emotions, establishing routines, and maintaining healthy habits, individuals with ADHD and anxiety can benefit from incorporating mindfulness practices into their daily lives. Mindfulness techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and grounding exercises can help individuals manage overwhelming emotions and reduce anxiety levels. For example, taking a few minutes each day to practice deep breathing can help individuals with ADHD and anxiety stay grounded and calm during moments of stress or anxiety.
Moreover, setting up a structured daily routine that includes designated time for work, relaxation, exercise, and self-care activities can provide a sense of stability and predictability for individuals managing ADHD and anxiety. This structured approach can help in reducing impulsivity, improving time management, and lowering stress levels throughout the day. For instance, creating a daily schedule that includes specific times for tasks, breaks, and leisure activities can help individuals with ADHD and anxiety feel more in control of their day-to-day responsibilities and emotions.
Furthermore, practising gratitude as a coping strategy can have a profound impact on the mental well-being of individuals with ADHD and anxiety. Taking time each day to reflect on and appreciate positive aspects of life , no matter how small, can shift focus from negative thoughts to positive experiences, promoting a more optimistic outlook and reducing anxiety levels. For example, keeping a gratitude journal where one writes down things they are thankful for daily can help individuals with ADHD and anxiety cultivate a mindset of gratitude and resilience in the face of challenges.

Self-Help Techniques for Individuals with ADHD and Anxiety
Incorporating self-help techniques into daily routines can significantly benefit individuals managing ADHD and anxiety. For instance, setting aside time for relaxation practices like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can effectively reduce stress levels and promote a sense of calm. Additionally, engaging in activities that encourage positive mental health, such as listening to music, practicing mindfulness, or finding moments of joy in daily life, can enhance overall well-being and resilience in the face of challenges. These simple yet powerful practices empower individuals to take an active role in their mental health and well-being, providing a sense of control over their symptoms.
Furthermore, establishing a structured routine that includes self-help activities can serve as a foundation for managing ADHD and anxiety symptoms. For example, creating a daily schedule that incorporates time for mindfulness exercises or engaging in hobbies that bring joy can help individuals maintain a sense of balance and stability. By prioritising self-care and mental health practices, individuals with ADHD and anxiety can build coping mechanisms that not only alleviate symptoms but also enhance their quality of life. Embracing these self-help techniques as part of a holistic approach to managing ADHD and anxiety can pave the way for long-term well-being and resilience in the face of daily challenges.
The Role of ADHD Coaching in Managing Anxiety
Individuals with ADHD often struggle with managing anxiety symptoms, and seeking support from an ADHD coach can be a game-changer in their journey towards better mental health. This strength-based approach to embracing and working with an ADHD diagnosis instead of battling against it, is an effective way to manage ADHD and anxiety. An ADHD coach plays a crucial role in helping individuals understand the connection between ADHD and anxiety, offering insights into how these conditions intertwine and influence each other. By shedding light on this relationship, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their strengths and challenges, and work towards managing them with targeted strategies and support.
In addition, an ADHD coach can provide tailored strategies and techniques to address specific challenges faced by those with ADHD and anxiety. One way an ADHD coach can help is by assisting individuals in creating a structured routine that includes dedicated time for relaxation and stress management activities, such as yoga or mindfulness exercises. This personalised approach can aid in alleviating anxiety symptoms and improving overall well-being by fostering a sense of control and stability in daily life.
Moreover, an ADHD coach can assist individuals in implementing practical techniques to cope with anxiety on a daily basis. For example, they may help create a structured routine that includes mindfulness practices, exercise, and regular breaks to alleviate anxiety symptoms. By working closely with an ADHD coach, individuals can learn how to identify triggers, manage their reactions during challenging situations, and develop resilience in the face of anxiety-provoking events. This personalised approach can empower individuals to take control of their anxiety and ADHD symptoms, leading to improved overall well-being and quality of life.
An ADHD coach can work with individuals to identify triggers that worsen their anxiety and ADHD symptoms, helping them develop coping mechanisms to navigate through challenging situations. By incorporating strategies, techniques and positive self-talk practices suggested by the coach and client, individuals can reframe negative thought patterns and build resilience in the face of anxiety-inducing circumstances. This collaborative effort between the individual and the coach promotes a proactive approach to managing anxiety and ADHD, empowering individuals to take charge of their mental health and effectively cope with daily stressors. Seeking support from an ADHD coach not only provides practical tools and strategies but also offers a supportive environment for individuals to explore their concerns and work towards sustainable improvements in managing their conditions.

The Role of Medication and Therapy
Medication and therapy are vital components in the treatment of ADHD and anxiety, offering a multifaceted approach to managing these conditions. While medication is instrumental in alleviating the core symptoms of ADHD, therapy, particularly cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT), is essential for addressing the intertwined anxiety symptoms that often accompany ADHD. For instance, individuals with ADHD may struggle with time blindness and emotional dysregulation, which can significantly impact their anxiety levels.
Moreover, the combination of medication and therapy has been shown to be highly effective in enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals grappling with ADHD and anxiety. In the case of ADHD, medication can assist in improving focus, impulse control, and hyperactivity, thereby reducing the stress and anxiety that these symptoms may trigger. Simultaneously, therapy, like CBT, equips individuals with valuable tools to challenge negative thought patterns, regulate emotions, and develop effective coping strategies for daily stressors.
By integrating medication and therapy into a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with ADHD and anxiety can experience significant relief and improvement in their symptoms. Medication addresses the neurological aspects of ADHD, while therapy delves into the psychological and behavioural components, fostering a holistic approach to managing these intertwined conditions. Working in tandem, medication and therapy empower individuals to navigate through the challenges posed by ADHD and anxiety, enhancing their overall well-being and quality of life.
Understanding and navigating the challenges of a neurotypical-ADHD relationship, including communication strategies, managing symptoms, seeking professional help, and celebrating the unique strengths of the relationship.
Impact on Neurotypical-ADHD Relationships
The impact of ADHD on neurotypical-ADHD relationships can be profound, influencing various aspects of the partnership. For instance, the symptoms of ADHD, such as distractibility, disorganization, and lack of focus, can significantly alter the relationship dynamics. Consider a scenario where an individual with ADHD struggles with distractibility, finding it challenging to maintain attention during conversations or important moments with their neurotypical partner. This can lead to feelings of neglect or lack of engagement, affecting the emotional connection in the relationship.
Moreover, undiagnosed ADHD can exacerbate the challenges within the relationship, potentially leading to conflict and dysfunction. Picture a situation where the neurotypical partner feels neglected or misunderstood due to their ADHD partner’s undiagnosed condition, which may lead to frustration and resentment. This can create a cycle of misunderstanding and miscommunication, further straining the relationship. Additionally, misconceptions about ADHD in relationships can contribute to a lack of empathy or support, adding to the complexity of the situation and potentially hindering the ability of the couple to navigate the challenges effectively.
Understanding the specific ways in which ADHD impacts the relationship dynamics is crucial for both partners to develop strategies and foster a supportive environment that addresses the unique challenges posed by the condition. By acknowledging these challenges, the couple can work together to find effective ways to mitigate the impact of ADHD on their relationship, fostering understanding, empathy, and resilience.

Understanding ADHD and its Impact on Relationships
ADHD can have a profound impact on the dynamics of a relationship, affecting both partners involved. For the individual with ADHD, the condition can lead to symptoms such as distractibility, disorganization, and a lack of focus, which can influence their ability to engage in the relationship effectively. These symptoms may cause the neurotypical partner to feel neglected or overlooked, creating a sense of disconnect and frustration within the relationship. For instance, a person with ADHD may struggle to remember important dates or conversations, which can make their partner feel unimportant or undervalued.
Moreover, ADHD can lead to misunderstandings and disagreements over responsibilities, such as household chores or financial management, which can create tension in the relationship. For example, a partner with ADHD may unintentionally overlook household tasks, leading to feelings of unfairness and frustration from the neurotypical partner. These instances can cause strain and conflict, highlighting the need for open communication and mutual understanding in neurotypical-ADHD relationships.
In addition, the challenges of ADHD can sometimes be misinterpreted by the neurotypical partner, leading to feelings of confusion or inadequacy. It’s important for both partners to recognise the impact of ADHD on the relationship and work together to find effective strategies for managing its effects. By understanding the complexities of ADHD and its influence on the relationship, both partners can navigate the challenges with empathy, patience, and a willingness to learn from each other’s perspectives.
Communication Strategies for a Successful Neurotypical-ADHD Relationship
When navigating a neurotypical-ADHD relationship, employing effective communication strategies is pivotal for the well-being of both partners. One valuable communication approach involves actively practising compassion and understanding to support each other through the unique challenges that ADHD can present. For instance, acknowledging the impact of distractibility and disorganization on the neurotypical partner and offering support and understanding can foster a more empathetic and nurturing relationship dynamic.
Moreover, managing conflicts in a neurotypical-ADHD relationship can be facilitated by consciously choosing battles wisely, demonstrating empathy, and refraining from intense nagging or criticism. For example, instead of getting embroiled in every minor disagreement, partners can proactively work towards a more peaceful coexistence by addressing only the most pertinent issues, thereby minimising unnecessary tension and fostering a more supportive environment. Furthermore, utilising positive language and expressing understanding towards the unique challenges associated with ADHD can significantly contribute to open and effective communication between partners, ultimately strengthening the bond of the relationship. By embracing these communication strategies, neurotypical-ADHD couples can cultivate an environment of understanding, empathy, and support, which are essential for a successful and fulfilling relationship.

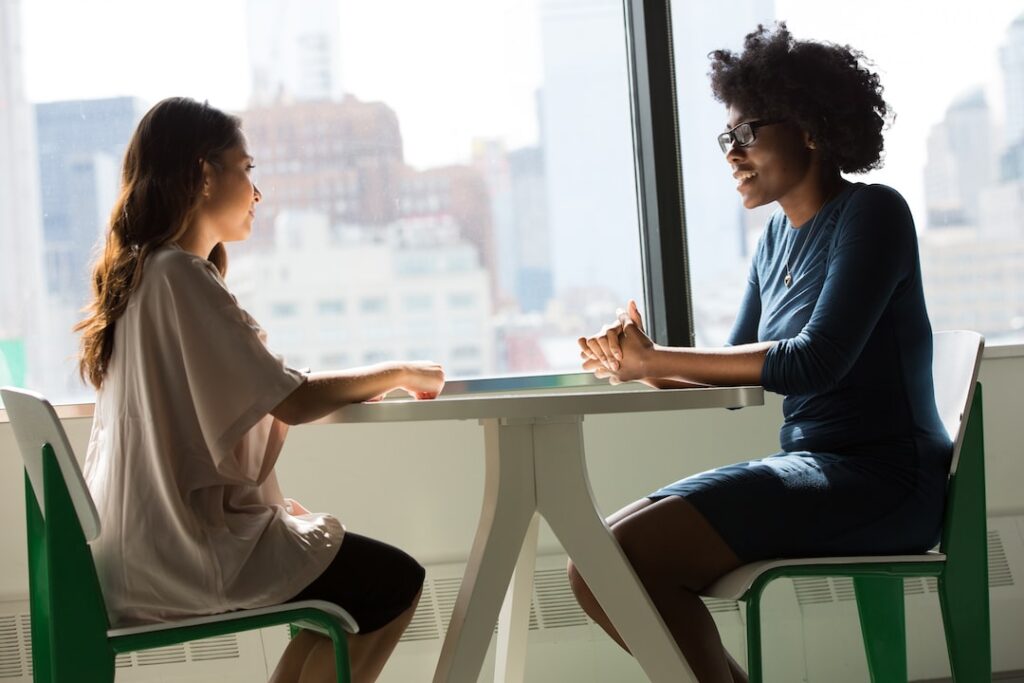
Managing ADHD Symptoms and Challenges in a Relationship
When it comes to managing ADHD symptoms and challenges in a relationship, it’s crucial to understand the unique aspects of ADHD and how they can impact the dynamics between partners. For instance, ADHD often leads to distractibility, disorganisation, and a lack of focus, which can pose challenges in a relationship. An example of this might be when a partner with ADHD struggles to maintain focus during important conversations or repeatedly forgets to complete household tasks, leading to frustration and misunderstandings.
In addition to understanding the impact of ADHD, it’s essential to implement smart solutions that can help navigate these challenges. For instance, using Nonviolent Communication, breaking the parenting dynamic, and learning about the specific ways in which ADHD affects the individual can be instrumental in fostering a supportive environment. An example of breaking the parenting dynamic could involve reframing communication and decision-making processes to ensure that both partners feel equal and respected in the relationship.
Furthermore, creating a peaceful and supportive atmosphere involves more than just understanding the condition; it also necessitates practical strategies and emotional support. For instance, scheduling private time for the relationship, slowing down to calm the mind, and choosing battles wisely can help reduce conflicts and promote a more harmonious connection. An example of this could be setting aside dedicated time for meaningful conversations and activities, allowing both partners to reconnect and strengthen their bond. Ultimately, by combining understanding, strategic solutions, and emotional support, partners can work together to effectively manage ADHD symptoms and challenges within their relationship.
Seeking Professional Help and Support
When it comes to managing the unique challenges of a neurotypical-ADHD relationship, seeking professional help and support is crucial. Educating oneself about ADHD and seeking guidance from a professional can significantly reduce the burden on the relationship. For instance, a couple struggling with the impact of ADHD on their relationship might benefit from consulting a therapist specialising in ADHD. This professional can offer tailored strategies and tools to help the couple navigate the challenges they are facing, providing them with a clearer understanding of how ADHD affects their relationship dynamic.
Moreover, both partners play a pivotal role in the success of the relationship, and seeking professional help can alleviate the challenges they may encounter. For example, a neurotypical partner might find it beneficial to seek individual therapy to gain a better understanding of ADHD and how it influences their relationship. Similarly, the partner with ADHD could benefit from therapy or coaching to develop strategies for managing their symptoms within the context of the relationship. By investing in professional support, both partners demonstrate a commitment to the relationship’s well-being and growth.
Additionally, it is advisable to seek professional assistance before the relationship is significantly impacted by ADHD-related issues. This proactive approach allows couples to address potential challenges early on, preventing these issues from escalating and causing lasting damage to the relationship. Seeking early intervention can provide couples with the tools and resources needed to effectively manage ADHD-related difficulties, fostering a stronger and more resilient relationship in the long run.

Celebrating the Strengths and Unique Qualities of Neurotypical-ADHD Relationships
Embracing the strengths and unique qualities of neurotypical-ADHD relationships is essential for fostering a positive and supportive environment. Honesty, openness, and understanding the ways in which behaviour can impact the relationship are key factors in celebrating the strengths of such relationships. Additionally, supporting the partner and working on building trust and openness can contribute to a more fulfilling and harmonious relationship.
For more blog articles, please click here.
[1] Source: https://add.org/six-secrets-to-a-happy-adhd-relationship Source: https://www.additudemag.com/adhd-divorce-rate-marriage-help Source: https://www.psychiatrist.com/news/3-ways-adhd-makes-romantic-relationships-more-challenging Source: https://sanespaces.com/2021/04/adhd-relationship-solutions-neurotypical
This blog article explores the challenges and strategies for being the best partner in a neurotypical-autistic relationship, including effective communication, understanding needs, and fostering a strong and healthy relationship.
Neurotypical Behaviour and Autism
Navigating a relationship between a neurotypical person and an autistic individual can present various challenges, including misunderstandings and frustrations stemming from differences in communication and social interaction. Autistic individuals often have intense special interests, including romantic relationships, which can sometimes be difficult for neurotypical partners to understand and relate to. For instance, an autistic individual may have a deep passion for a specific topic or hobby, and their neurotypical partner might struggle to comprehend the extent of this interest, leading to feelings of disconnect or isolation. Therefore, it is essential for neurotypical partners to recognise and appreciate the intensity and significance of these special interests, fostering an environment of support and encouragement.
In addition, it is crucial to dispel myths about autism, such as the misconception that autistic individuals lack empathy or do not experience emotions. In reality, autistic people can fall in love and are very empathetic, but they may struggle with expressing emotions and may withdraw during conflict. Therefore, neurotypical partners should approach emotional expression with patience and understanding, recognising that their autistic partner may require additional time and support to convey their feelings effectively. By acknowledging and accepting the diverse ways in which emotions are expressed and experienced within the autistic community, both partners can cultivate a deeper understanding and appreciation for each other’s emotional landscapes, enhancing the overall connection and intimacy in the relationship.
Communication in Neurotypical-Autistic Relationships
In neurotypical-autistic relationships, effective communication plays a crucial role in fostering understanding and harmony. One key strategy is the use of direct and clear communication, especially when one partner is neurodivergent. For instance, a neurotypical partner may need to be direct in expressing their thoughts and emotions, ensuring that their autistic partner comprehends their perspective. By being straightforward and explicit in their communication, the neurotypical partner can help minimise misunderstandings and create a conducive environment for open dialogue.
Moreover, active listening is an essential aspect of effective communication in these relationships. Both partners should actively engage in listening to each other, showing empathy, and acknowledging each other’s viewpoints. This not only promotes mutual understanding but also fosters a sense of validation and respect within the relationship. Additionally, reducing assumptions can prevent misinterpretations and conflicts, allowing both partners to express themselves freely without the burden of preconceived notions or biases.
It’s also crucial to recognise the impact of sudden changes on autistic individuals. For example, an unexpected alteration in plans or routines can lead to heightened anxiety for the autistic partner. Understanding this need for stability and predictability can help the neurotypical partner navigate the relationship more sensitively, thereby strengthening the bond and trust between them.
Support and Accommodation for Neurotypical Needs
Accommodating sensory sensitivities and social settings is crucial for supporting neurodivergent partners within the relationship. Sensory sensitivities can manifest in various ways for autistic individuals, such as being hypersensitive to loud noises, bright lights, or certain textures. For instance, a neurotypical partner can help create a sensory-friendly environment by using dimmer lights, reducing background noise, or avoiding scratchy fabrics, thus contributing to the comfort and well-being of their autistic partner.
In addition to sensory accommodations, it’s imperative to avoid fostering a parent-child dynamic in relationships with autistic individuals, instead, approaching the partnership as equals and respecting each other’s autonomy and agency. This can be demonstrated by involving the autistic partner in decision-making processes, acknowledging their opinions, and valuing their independence. By doing so, both partners can contribute to a more balanced and respectful dynamic within the relationship.
Addressing moments of overwhelm with compassion and understanding towards the neurodivergent partner can significantly contribute to a supportive and harmonious relationship. For example, if an autistic individual experiences sensory overload in a crowded social setting, a neurotypical partner can offer understanding and support by creating a safe space for them to decompress, whether it’s finding a quiet corner or leaving the environment altogether. This understanding and support can help the autistic partner feel respected and cared for during challenging moments.

Building a Strong and Healthy Relationship
When seeking to build a strong and healthy relationship with an autistic individual, it’s crucial to recognise the significance of seeking therapy services that are specifically tailored to support romantic relationships on the autism spectrum. These therapy services can offer invaluable guidance and assistance in navigating the unique dynamics of such partnerships, providing a safe space for both partners to express their needs, concerns, and aspirations. Through therapy, partners can learn effective communication strategies, gain a deeper understanding of each other’s unique perspectives, and develop the necessary tools to address challenges that may arise within the relationship.
Furthermore, accommodating the needs and desires of both neurotypical and autistic partners is fundamental for fostering emotional intimacy and ensuring that the relationship is fulfilling for all involved. This might involve creating an environment that respects sensory sensitivities, understanding the impact of intense special interests on the relationship, and acknowledging the importance of clear and direct communication for neurodivergent partners. For instance, a neurotypical partner may need to make adjustments to social settings, such as choosing quieter venues or limiting the duration of outings to accommodate the sensory sensitivities of their autistic partner. By doing so, both partners demonstrate their commitment to understanding and supporting each other, ultimately strengthening the bond between them.
Navigating Intense Special Interests and Romantic Relationships
It’s essential to recognise that intense special interests can have a significant impact on romantic relationships involving an autistic individual. For example, an autistic person may have a deep passion for a specific topic or activity, such as collecting vintage records or studying astronomy. This intense focus can sometimes lead to challenges in the relationship, as the neurotypical partner may find it difficult to relate to or understand the depth of their partner’s interest. However, by acknowledging the positive aspects of these intense interests, such as the passion and dedication they represent, both partners can work towards a mutual understanding and respect for each other’s unique passions.
In addition to the challenges, there are also benefits to navigating these intense special interests in the relationship. For instance, the neurotypical partner can learn from the autistic individual’s focused dedication and commitment, which can inspire a similar level of devotion in their own pursuits. By openly discussing and sharing their respective interests, the couple can find common ground and even discover new activities that they both enjoy, thus strengthening their bond and creating shared experiences. Ultimately, fostering an environment of encouragement and support for each other’s individual passions can contribute to the overall health and happiness of the relationship.

Overcoming Autism Relationship Problems
When it comes to relationships with autistic individuals, various challenges can arise, impacting the dynamics between partners. For instance, reading social cues, managing anxiety, and addressing sensory issues can be particularly difficult for autistic individuals. These challenges can lead to misunderstandings and frustrations in the relationship, as the neurotypical partner may struggle to understand and navigate these aspects of their partner’s experience. However, it’s important for both partners to recognise the impact of these challenges and work together to find effective strategies for overcoming them.
For example, a common challenge in autistic-neurotypical relationships is the interpretation of social cues. Autistic individuals may find it challenging to read non-verbal communication and subtle social hints, leading to misunderstandings or feelings of isolation. In such cases, the neurotypical partner can play a supportive role by clearly expressing their thoughts and feelings, thus fostering open communication and mutual understanding within the relationship. By recognising the impact of these challenges and proactively addressing them, both partners can navigate these difficulties more effectively, strengthening their bond and fostering a supportive environment for personal growth.
Another aspect of overcoming relationship challenges involves building new social connections and coping with rejection as an autistic adult. This can be vital for fostering resilience and a sense of belonging within the broader social context. For instance, engaging with the neurodivergent community, following personal interests, and scheduling relaxation time are all ways in which an autistic individual can build new social connections and find a supportive network. By doing so, they can not only find understanding and acceptance outside the relationship but also bring a sense of fulfilment and balance into their personal lives, which can positively impact the relationship dynamic. Therefore, recognising the importance of these aspects and supporting each other in navigating them can significantly contribute to the strength and resilience of the relationship.
Click here for more blog posts.
This article explores the connection between autism, ADHD, and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome, highlighting the shared symptoms, co-occurrence of conditions, available treatments, and resources for support.
Understanding Autism, ADHD, and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
Autism, ADHD, and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome are complex conditions that have significant impacts on individuals’ lives. Autism is often associated with challenges in social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviours, while ADHD is characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. On the other hand, Ehlers Danlos Syndrome encompasses a group of genetic disorders affecting connective tissues, leading to a range of symptoms, including joint hypermobility.
Individuals with autism, ADHD, and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome commonly experience various challenges and overlapping symptoms. For instance, individuals with autism may exhibit sensory sensitivities, making it difficult for them to process and respond to sensory information like touch, sound, and light. Similarly, individuals with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome may also experience sensory issues, such as heightened sensitivity to pain and touch due to their connective tissue disorder. Understanding the shared symptoms and challenges among these conditions is crucial in providing comprehensive and effective support and care for individuals affected by them.
Moreover, individuals with ADHD often struggle with executive function skills such as planning, organisation, and time management. These challenges can significantly impact their daily lives, education, and work. In the same vein, individuals with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome, especially those with joint hypermobility, may also face difficulties in motor skills and coordination due to the instability of their joints. Therefore, recognising these commonalities among the conditions can aid in the development of tailored interventions and therapies to address the diverse needs of individuals with autism, ADHD, and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome.
The Connection: Joint Hypermobility and Neurodivergence
The connection between joint hypermobility and neurodivergence is a significant area of research, shedding light on the overlapping symptoms and conditions associated with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome and autism. Studies have found that individuals with joint hypermobility , Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS), and hypermobility spectrum disorders are more likely to be autistic, highlighting a potential link between these conditions. For instance, a study by BSMS revealed that over 50% of neurodivergent participants had elevated levels of hypermobility, suggesting a strong association between joint hypermobility and autism.
Moreover, neurodivergent individuals with joint hypermobility have reported experiencing more symptoms of pain and dysautonomia. This overlap of symptoms indicates the complexity of managing these conditions and the need for tailored medical intervention. Additionally, the Beighton Scoring System, which is a standard physical assessment to identify joint hypermobility, is recommended for use in identifying joint hypermobility in autistic individuals. This system can be an essential tool for healthcare professionals to diagnose and understand the extent of joint hypermobility in individuals with autism, enabling them to provide appropriate care and support.
The high prevalence of joint hypermobility in autistic individuals and the increased symptoms of pain and dysautonomia highlight the need for greater awareness and understanding of this association. It is crucial for medical practitioners to recognise the interconnection between joint hypermobility and neurodevelopmental conditions like autism and to develop targeted interventions to address the specific needs of individuals with these overlapping conditions. This comprehensive approach can lead to improved outcomes and better quality of life for those affected by joint hypermobility and neurodivergence.
Co-Occurrence of Conditions
The co-occurrence of Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS) and autism is a topic of growing interest and concern within the medical and research communities. Studies have shown that there is a higher prevalence of EDS in individuals with autism compared to the general population, indicating a potential link between the two conditions. This presents a significant challenge for individuals and their families, as the simultaneous management of symptoms associated with both EDS and autism can be complex and demanding.
For instance, many autistic individuals with EDS often experience overlapping symptoms, such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), learning disorders, sensory sensitivities, and mental health issues. This overlap can exacerbate the challenges faced by individuals, potentially impacting their daily functioning and overall quality of life. Moreover, both conditions are associated with coordination problems, sensory issues, autonomic dysregulation, and immune dysregulation, further complicating the clinical picture for individuals living with these co-occurring conditions. This underscores the need for a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to address the diverse and interconnected symptoms arising from the co-occurrence of EDS and autism.
It is crucial for healthcare professionals to be well-informed about the potential co-occurrence of these conditions, ensuring that individuals receive accurate diagnoses and appropriate support. Moreover, families and caregivers should be equipped with the necessary resources and guidance to navigate the complexities of managing these co-occurring conditions effectively. By recognising and addressing the shared symptoms and challenges associated with EDS and autism, it becomes possible to provide more targeted and holistic care to individuals affected by these conditions. [2].
Available Treatments and Therapies
When it comes to individuals affected by autism, ADHD, and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome, it’s essential to understand that they may require similar therapies and treatments due to the overlapping symptoms and challenges associated with these conditions. For instance, individuals with autism often benefit from behavioural therapies, speech therapy, and occupational therapy to address communication difficulties and sensory issues, which can also be beneficial for individuals with ADHD and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome. Moreover, those with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome may require physical therapy and pain management strategies to address joint hypermobility and chronic pain, which can also be beneficial for individuals with autism and ADHD who experience similar issues [4].
Furthermore, management of symptoms can be achieved with support and advice from healthcare professionals, including a multidisciplinary approach involving specialists such as neurologists, geneticists, occupational therapists, and psychologists. For example, individuals with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome and autism may benefit from a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their physical, neurological, and psychological needs. This could include tailored exercise regimens to improve joint stability, cognitive behavioural therapy to address anxiety or depression, and medications to manage autonomic dysregulation [4].
In addition, there is a pressing need for specific recognition, research, and treatments for the association between Ehlers Danlos Syndrome and autism. Currently, there is a lack of specific guidelines or targeted interventions for individuals who have both conditions. Therefore, increasing awareness among healthcare professionals and conducting further research to understand the unique needs of individuals with both Ehlers Danlos Syndrome and autism is crucial to developing effective treatments and improving the quality of life for these individuals. These efforts can lead to the development of tailored interventions that address the complex interplay of symptoms and provide the necessary support for individuals affected by the co-occurrence of these conditions.

Support and Resources
The Ehlers-Danlos Society has been actively working to increase awareness of the intricate relationship between autism and joint hypermobility. By collaborating with experts like Dr. Carolina Baezo-Velasco, who is an expert in Ehlers Danlos Syndrome and Autism, the society has been able to provide valuable insights and resources for individuals and families affected by these conditions. Their efforts have been instrumental in shedding light on the co-occurrence of Ehlers Danlos Syndrome and autism, offering support and guidance to those navigating these complex conditions.
For parents of children with autism who exhibit symptoms consistent with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome, obtaining a proper diagnosis and seeking appropriate treatment is crucial. The overlap of symptoms between these two conditions necessitates careful consideration and evaluation. By being proactive in seeking medical attention, parents can ensure that their child receives the necessary support and interventions tailored to their specific needs. This proactive approach can significantly impact the child’s well-being and overall quality of life, empowering them to better manage the challenges associated with the co-occurring conditions.
Furthermore, for individuals and families seeking a deeper understanding of Ehlers Danlos Syndrome in the context of autism, a wealth of resources is readily available. These resources encompass educational materials, support networks, and guidance for navigating the unique challenges posed by the co-occurrence of these conditions. Access to reliable information and support can be invaluable in empowering individuals and families to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of living with autism and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome.
For more blog posts, please click here.
Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) are neurodevelopmental disorders that affect millions of people worldwide. Traditionally, these conditions have been studied predominantly in boys and men. However, recent research has begun to shed light on how they manifest differently in girls and women. This blog post will delve into the complex world of cooccurring ADHD and autism in females, a topic that has been largely overlooked until now.
Understanding Autism and ADHD
Before we delve into the specifics of cooccurring ADHD and autism in girls and women, it’s essential to understand what these conditions entail. Autism is a developmental disorder characterised by difficulties with social interaction, communication challenges, and repetitive behaviours. On the other hand, ADHD is marked by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity that interfere with functioning or development.
Historically, these conditions were considered separate entities with distinct diagnostic criteria. However, recent studies have shown a significant overlap between ASD and ADHD symptoms leading to a high prevalence of cooccurring ADHD and autism. This shift in understanding has prompted researchers and clinicians to explore the connections between the two conditions more deeply, with a focus on tailored interventions and support for individuals who may experience symptoms of both. Understanding the interplay between ADHD and autism spectrum disorder can lead to more effective strategies for diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected by these complex neurodevelopmental conditions.

Cooccurring ADHD and Autism in Girls and Women
Research indicates that females with ASD are more likely to have cooccurring ADHD than their male counterparts. This dual diagnosis can exacerbate the challenges faced by these individuals as they navigate social interactions, academic performance, emotional regulation, among other areas of life.
The issue of underdiagnosis and misdiagnosis of certain disorders in girls and women is indeed a critical concern that has far-reaching implications. Societal stereotypes often associate certain disorders with males, leading to a lack of recognition and understanding when these disorders manifest in females. Additionally, the differences in symptom presentation between genders can further exacerbate the problem, resulting in many girls and women remaining undiagnosed or misdiagnosed for extended periods of time.
As a consequence of this delay in diagnosis, individuals may face significant mental health challenges, such as heightened anxiety and depression stemming from unaddressed struggles. The toll of navigating life with undiagnosed or misdiagnosed disorders can be immense, impacting daily functioning, personal relationships, and overall well-being. It is imperative to raise awareness about these disparities in diagnosis and to advocate for improved understanding and recognition of the diverse ways in which these disorders can manifest across different genders. By facilitating earlier and more accurate identification, individuals can receive the support and interventions they need to effectively manage their conditions and mitigate the associated mental health implications.
Some symptoms of comorbid ADHD and autism can include:
- Social Challenges: Girls and women with cooccurring ADHD and autism may struggle with social interaction, finding it hard to understand and interpret social cues. They might also find it challenging to form and maintain friendships.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Individuals may experience heightened sensitivities to sensory stimuli, including light, sound, touch, and taste. This can lead to discomfort and distress in everyday environments.
- Repetitive Behaviours: Engaging in repetitive movements or actions, such as hand-flapping or rocking, is common among those with cooccurring ADHD and autism. These behaviours can serve as self-soothing mechanisms.
- Difficulty with Transitions: Changes in routine or unexpected events can be particularly distressing for individuals with cooccurring ADHD and autism, leading to anxiety and meltdowns.
- Attention and Executive Functioning Challenges: Problems with sustained attention, organisation, and task completion are typical. Additionally, difficulties in planning and prioritising tasks may be apparent.
The Gender Gap: Why Are Girls and Women Overlooked?
One reason why girls and women might be overlooked when it comes to diagnosing cooccurring ADHD and autism is the gender bias in the diagnostic criteria. These criteria were developed based on studies conducted predominantly on boys and men, leading to a skewed understanding of how these conditions present in females.
Girls with ASD often exhibit less obvious signs compared to boys. They may have fewer repetitive behaviours and may be better at masking their social communication difficulties by mimicking others’ behaviours. Similarly, girls with ADHD are more likely to present with inattentiveness rather than hyperactivity, which can be mistaken for daydreaming or lack of interest.
Furthermore, societal expectations and norms often pressure girls and women to conform, leading them to develop coping mechanisms that mask their symptoms. This ‘camouflaging’ can make it even more challenging for clinicians to identify these conditions.

The Importance Of Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for individuals with cooccurring ADHD and autism. It allows for timely access to therapies and supports that can significantly improve their quality of life. For girls and women, this could mean avoiding years of feeling ‘different’ without knowing why, thus preventing the onset of secondary mental health issues.
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in recognising and understanding the gender differences in symptom presentation for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). It is important for them to be aware that the manifestation of these conditions can vary between boys and girls, men and women. By being knowledgeable about the unique ways in which ASD and ADHD may present in different genders, healthcare professionals can ensure more accurate diagnoses and better tailored interventions.
Moreover, it is essential for healthcare professionals to consider the possibility of dual diagnoses when assessing patients with complex profiles. This means understanding that an individual may present symptoms that align with more than one condition, such as having both ASD and ADHD. Recognizing the potential for comorbidities is vital in providing comprehensive care and support to patients.
In summary, raising awareness among healthcare professionals about gender-specific symptomatology for ASD and ADHD, as well as the potential for dual diagnoses, can lead to more effective and personalised care for individuals with these conditions.”
Conclusion
Cooccurring ADHD and autism in girls and women is a complex issue that requires further research and awareness. By understanding how these conditions manifest differently in females compared to males, we can ensure that they receive accurate diagnoses earlier in life. This will enable them to access appropriate supports sooner, improving their overall wellbeing.
In conclusion, it’s not a matter of one or the other but recognising that both can coexist. With increased awareness among healthcare providers, educators, parents, and society at large; we can ensure that girls and women with cooccurring ADHD and autism are identified early on so they can receive the help they need to thrive.
For more information on ADHD and Autism-related topics, please take a look at my other blog posts, which can be found here.
This article explores the importance of seeking a formal diagnosis for ADHD and/or Autism, discussing the benefits, advantages and disadvantages.
The Importance of Seeking a Formal Diagnosis for ADHD/autism
Seeking a formal diagnosis for ADHD or autism is both beneficial and essential for a multitude of reasons. A formal diagnosis not only provides a better understanding of the specific challenges and needs associated with these conditions but also opens the door to various benefits. For instance, being diagnosed with both ASD and ADHD allows for finding treatments and coping strategies that work for both conditions, leading to validation and self-acceptance.
Moreover, a formal diagnosis enables individuals to access appropriate support and accommodations tailored to their specific challenges and needs. It also makes them eligible for specialised services and therapies, along with legal protections and accommodations. This comprehensive understanding and access to support and accommodations can significantly improve an individual’s quality of life and well-being. Furthermore, it can reduce self-blame and improve family and couple relationships, fostering a supportive environment for individuals with ADHD or autism.
Understanding a Formal Diagnosis of ADHD or Autism
Seeking a formal diagnosis for ADHD or autism offers a multitude of benefits that can significantly impact an individual’s life. One of the most crucial advantages is gaining access to tailored support and accommodations that specifically address the challenges and needs associated with these conditions. For instance, with a formal diagnosis, individuals can receive personalised interventions, therapy, and educational support that are specifically designed to address their unique symptoms and difficulties.
Moreover, a formal diagnosis plays a pivotal role in fostering validation and self-acceptance. It allows individuals to gain a deeper understanding of their condition, which can lead to a sense of acceptance, empowerment, and relief. Armed with a formal diagnosis, individuals can embark on a journey to find treatments and coping strategies that are tailored to both ADHD and autism, ultimately contributing to an improved quality of life and overall well-being.
Seeking a formal diagnosis opens the door to a range of specialised services and therapies that may not have been accessible otherwise. This can include access to occupational therapy, speech therapy, and other targeted interventions that can significantly enhance an individual’s daily functioning and quality of life. Additionally, a formal diagnosis paves the way for legal protections and accommodations, such as workplace accommodations and educational support, ensuring that individuals receive the necessary resources to thrive in various aspects of their lives.
It is important to note that seeking a formal diagnosis not only benefits the individual directly, but it also has a positive impact on their support system. By increasing access to help and support, reducing self-blame, and improving family and couple relationships, a formal diagnosis can foster a more supportive and understanding environment for the individual, ultimately contributing to their overall well-being and success.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Seeking a Formal Diagnosis
There are many benefits for diagnosing one’s ADHD and/or autism. Firstly, a formal diagnosis provides validation and self-acceptance. It allows individuals to understand themselves better, including their personal strengths and needs. This understanding can be empowering and can lead to the adoption of coping strategies that are tailored to their specific challenges. By embracing a formal diagnosis, individuals can also access a supportive network of professionals and peers who understand their experiences, thereby reducing feelings of isolation and fostering a sense of belonging within a community.
In addition to the personal benefits, a formal diagnosis enables individuals to access appropriate support and accommodations. This can be instrumental in navigating challenges related to ADHD or autism in various aspects of life, including education, employment, and social interactions. Furthermore, a diagnosis may open the door to specialised services and therapies that are specifically designed to address the unique needs of individuals with ADHD or autism. These services can range from behavioural therapies to occupational therapy, speech therapy, and other interventions that are tailored to the individual’s diagnosis, potentially leading to improved outcomes and overall well-being.
However, it is essential to acknowledge the potential disadvantages associated with seeking a formal diagnosis. For instance, mandatory disclosure of a diagnosis in certain careers can lead to stigmatisation or discrimination, making it a challenging decision for some individuals. The process of obtaining a formal diagnosis can be costly and time-consuming, often involving long waitlists for assessments. These barriers can create additional stress and financial strain for individuals seeking a diagnosis. Therefore, while the benefits of a formal diagnosis are substantial, it is crucial to weigh them against the potential challenges and make an informed decision based on individual circumstances and needs.
The Growing Trend of Self-Diagnosis
The internet and social media have significantly contributed to the increasing trend of self-diagnosis of autism and ADHD. People are now able to access a wealth of information, personal experiences, and self-assessment tools online, leading them to recognise symptoms and traits that align with ADHD or autism. This accessibility has empowered individuals to self-reflect and self-identify, especially when traditional diagnostic processes may be inaccessible due to long waitlists, financial constraints, or lack of understanding from healthcare providers.
Moreover, the debate surrounding self-diagnosis revolves around the validity and implications of this practice. While some argue that self-diagnosis can lead to misinterpretation and may not account for the full spectrum of symptoms and impact, others advocate for its empowering nature. For many individuals, self-diagnosis serves as a crucial first step towards understanding themselves better and seeking the support they need. It creates a sense of community and solidarity among neurodivergent individuals, allowing them to share experiences, coping strategies, and insights, ultimately fostering a supportive environment for those who may feel isolated or misunderstood.
One example of the positive impact of self-diagnosis is the way it has provided an avenue for individuals who would otherwise have been overlooked to recognise their neurodivergent traits. This is especially true for women, non-binary individuals, and people of colour who historically have faced challenges in obtaining formal diagnoses due to biases and misconceptions amongst healthcare professionals. Through self-diagnosis, these individuals can gain a better understanding of themselves and their needs, enabling them to access relevant support and accommodations, and connect with others who share similar experiences, thereby reducing the sense of isolation and offering a platform for advocacy and empowerment within the neurodivergent community.
Gender Disparities in Diagnosis
Gender disparities in the diagnosis of autism and ADHD are quite significant, with boys being diagnosed at an average age of 8, while girls typically receive a diagnosis around the age of 12. This delay in diagnosis for girls can have profound implications, as it may result in unmet needs and challenges going unnoticed or unaddressed. Research has revealed that prevalence rates of autism in women are higher than previously thought, indicating that there may be a significant number of undiagnosed women and girls on the autism spectrum who could benefit from a formal diagnosis.
For women who receive a formal diagnosis, the advantages are multifaceted. Firstly, it can bring a sense of relief, providing an explanation for the challenges they have faced throughout their lives. This relief is often accompanied by a newfound clarity about their strengths and difficulties, which can be empowering and aid in self-acceptance. Moreover, a formal diagnosis can foster a sense of belonging, as it connects women with a community of individuals who share similar experiences and can provide support and understanding. Importantly, a formal diagnosis also allows women to learn coping strategies tailored to their specific needs, enhancing their ability to navigate everyday life and relationships.
Women may arrive at a formal diagnosis through various pathways. Some women are initially diagnosed with other conditions, such as anxiety or depression, before eventually receiving a diagnosis of autism or ADHD. Others may have a family member who receives a diagnosis, which prompts them to explore the possibility of their own neurodevelopmental differences. Additionally, the widespread availability of information on the Internet has empowered many women to research and recognise their own traits and challenges, leading them to seek a formal diagnosis to gain a deeper understanding of themselves.
Conclusion
Seeking a diagnosis for ADHD or autism brings a multitude of benefits that significantly impact an individual’s life. One of the primary advantages is the provision of a better understanding of the specific challenges and needs associated with these conditions. For instance, a formal diagnosis can shed light on the unique ways in which ADHD or autism may affect an individual’s daily life, social interactions, and emotional well-being. This understanding serves as a crucial foundation for developing tailored support strategies and interventions, which can significantly improve the individual’s quality of life. Additionally, a formal diagnosis allows individuals to gain insights into their strengths, enabling them to harness these positive attributes as they navigate their neurodiverse journey.
Moreover, seeking a formal diagnosis is essential for accessing appropriate support and accommodations. Individuals with ADHD or autism often encounter various challenges in academic, professional, and social settings. Through a formal diagnosis, they become eligible for specialised services and therapies specifically designed to address their unique needs. This can encompass a spectrum of interventions, including cognitive behavioural therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training. Furthermore, a formal diagnosis also provides individuals with legal protections and accommodations, ensuring they receive the necessary support and adjustments in educational and workplace settings. These accommodations can play a pivotal role in mitigating the impact of ADHD or autism-related challenges, promoting a more inclusive and enabling environment for individuals with neurodevelopmental differences.
Additionally, the process of seeking a formal diagnosis offers a profound sense of validation and self-acceptance. It goes beyond the mere acquisition of a diagnostic label; it signifies the recognition and affirmation of an individual’s experiences and challenges. This validation can lead to reduced self-blame and enhanced self-understanding, empowering individuals to embrace their neurodivergent identity with confidence. Furthermore, a formal diagnosis opens the door to a supportive community, enabling individuals to connect with others who share similar experiences and create a network of understanding and solidarity. Ultimately, the journey of seeking a formal diagnosis is not just about obtaining a label; it is a transformative process that fosters empowerment, self-compassion, and a sense of belonging.
For more blog posts, please click here.
[1] Source: https://www.webmd.com/add-adhd/adult-adhd-autism
An overview of sleep issues in individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), including their prevalence, impact, contributing factors, and strategies for improvement.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Sleep: An Overview
Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often experience a high prevalence of sleep problems, which can have a significant impact on their well-being and that of their families. In fact, nearly 80% of autistic preschoolers experience disrupted sleep, highlighting the widespread nature of this issue. It is not uncommon for people with ASD to struggle with insomnia, wake up frequently during the night, and even experience sleep apnea, leading to a myriad of sleep-related challenges.
Moreover, the disruptive nature of these sleep problems can extend beyond the individuals with ASD themselves and impact their families as well. For instance, parents of autistic children often face significant challenges in managing the sleep difficulties of their children, which can lead to increased stress and fatigue. The impact on daily routines can be substantial, affecting the overall quality of life for both the individuals with ASD and their families. Managing these sleep issues becomes an integral part of the overall care and support for individuals with ASD, highlighting the need for effective strategies and interventions to address this prevalent concern.
These challenges can lead to disruptions in daily routines and affect the overall quality of life for individuals with ASD and their families. It is essential to understand the specific nature of these sleep issues and their impact to develop tailored interventions that effectively support individuals with ASD in achieving better sleep quality and overall well-being.
Understanding Sleep Issues in Individuals with Autism
The common sleep issues in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are multifaceted and can significantly impact the daily lives of both the individuals with ASD and their families. One of the most prevalent sleep issues experienced by individuals with ASD is difficulty falling asleep, which can lead to prolonged periods of restlessness and frequent awakenings during the night. This can result in fatigue, irritability, and challenges in focusing during the day, affecting the overall quality of life.
Furthermore, the specific sleep issues experienced by individuals with ASD, such as difficulty staying asleep and restless sleep, can exacerbate the core symptoms of autism, including social communication deficits and repetitive behaviours. For example, the lack of quality sleep can contribute to increased irritability and heightened repetitive behaviours, making it challenging for individuals with ASD to engage in social interactions and daily activities. The impact of disrupted sleep on individuals with ASD underlines the critical need for effective strategies and interventions to address these issues comprehensively.
In addition, the irregular melatonin levels in individuals with ASD can further complicate their sleep patterns, making it essential for families and caregivers to have access to reliable guides and resources to navigate these challenges effectively. The disruptive nature of sleep problems for autistic adults and children underscores the importance of tailored support and interventions to promote better sleep hygiene and overall well-being for individuals with ASD and their families.
Factors Contributing to Sleep Problems in Individuals with ASD
The prevalence of sleep problems in individuals with ASD can be attributed to a multitude of factors, including irregular melatonin levels, which play a significant role in regulating sleep-wake cycles. Melatonin, a hormone produced by the pineal gland, helps signal the body that it’s time to sleep, and individuals with ASD often exhibit irregularities in melatonin secretion, leading to difficulties in falling asleep and staying asleep.
Moreover, individuals with ASD frequently experience challenges with relaxing and winding down, which can further exacerbate their sleep issues. The sensory sensitivities commonly associated with ASD, such as heightened sensitivity to noise, light, or touch, can make it challenging for individuals to unwind and prepare for sleep. These difficulties in relaxation can contribute to prolonged sleep onset latency and fragmented sleep patterns, impacting the overall quality of sleep.
In addition to these factors, co-occurring medical conditions, such as anxiety, depression and ADHD can significantly influence the sleep patterns of individuals. Research indicates that gastrointestinal problems, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and anxiety disorders are prevalent among individuals with ASD and can contribute to sleep disturbances. It’s essential for healthcare professionals and caregivers to recognise and address these co-occurring conditions when developing tailored interventions to improve sleep in individuals with ASD. Understanding the intricate interplay of these factors is vital in devising comprehensive strategies to enhance the sleep quality of individuals with ASD, thereby promoting their overall well-being.
Impact of Sleep Issues on Individuals with Autism
The impact of sleep issues on individuals with autism extends beyond mere fatigue and restlessness. It can significantly exacerbate core features of autism. For example, a child with autism who experiences disrupted sleep may struggle even more with social interactions, leading to increased feelings of isolation and frustration. This can further hinder their ability to develop and maintain meaningful relationships with peers and family members, impacting their overall quality of life.
Moreover, the relationship between sleep and autism features is bidirectional, as addressing sleep problems has been shown to yield remarkable improvements in social communication, attention, and repetitive behaviours in children with autism. For instance, a study revealed that implementing a consistent sleep routine and using melatonin supplements led to reduced repetitive behaviours and improved attention in children with autism. This underscores the critical role of addressing sleep issues in enhancing the overall well-being and functioning of individuals on the autism spectrum. By prioritising healthy sleep patterns, individuals with autism can experience positive changes in their daily interactions, cognitive abilities, and emotional regulation, contributing to an improved quality of life.

Interventions to Improve Sleep
Establishing a consistent sleep routine is crucial for individuals with ASD, as it can help regulate their circadian rhythms and improve overall sleep quality. This routine may include a set bedtime, calming activities before bed, and creating a soothing sleep environment. For example, using low lighting, calming music, or a weighted blanket, can help individuals feel more relaxed and ready for sleep. By following a consistent routine, individuals with autism can develop a sense of predictability and security, which can significantly aid in improving their sleep patterns.
In addition to addressing sensory sensitivities, the use of melatonin supplements has shown promise in helping people with autism sleep better. Melatonin is a hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle, and individuals with ASD often have irregular melatonin levels. By consulting with a healthcare professional, individuals with autism and their families can explore the appropriate use of melatonin supplements to support their sleep.
Furthermore, research-backed strategies and interventions play a vital role in addressing the specific sleep needs of individuals with ASD. These strategies may include behavioural interventions, such as implementing a bedtime routine, cognitive-behavioural therapy for insomnia, ASD Coaching, or environmental modifications to create a sleep-conducive atmosphere. By tailoring interventions to the individual’s unique needs and preferences, it becomes possible to create an effective approach to improving sleep in individuals with autism. Research from Spectrum, a leading source of news and expert opinion on autism research, highlights the significance of individualised interventions in promoting better sleep outcomes for individuals with ASD. Such personalised strategies can lead to substantial improvements in sleep quality and overall well-being.

Sleep Hygiene Tips for Individuals with ASD
In addition to maintaining a consistent bedtime, creating a quiet sleeping environment, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and large meals before bedtime, there are other crucial sleep hygiene tips that can benefit individuals with ASD. One important tip is to establish a calming pre-sleep routine, such as engaging in relaxing activities like reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practising deep breathing exercises. This routine can help individuals with autism unwind and transition into a more relaxed state before bedtime, making it easier for them to fall asleep.
Furthermore, it’s essential to ensure that the sleeping environment is conducive to quality sleep. This can involve using blackout curtains to block out light, reducing noise levels, and maintaining a comfortable room temperature. For individuals with autism who may have sensory sensitivities, using weighted blankets or specific types of bedding that provide a comforting sensory input can also promote better sleep.
Incorporating these additional sleep hygiene tips alongside the foundational practices of maintaining a consistent bedtime and avoiding stimulants can provide a comprehensive approach to enhancing the sleep quality of individuals with autism. By tailoring the sleep environment and pre-sleep routine to accommodate the specific needs of individuals with ASD, it becomes possible to mitigate the impact of sleep difficulties and promote better overall well-being.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the common sleep issues in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD)? Common sleep issues in individuals with ASD include difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, and restless sleep, which can have a significant impact on their daily routines and overall well-being.
- What factors contribute to sleep problems in individuals with ASD? Factors contributing to sleep problems in individuals with ASD include irregular melatonin levels, difficulties with relaxing and winding down, and co-occurring medical conditions, anxiety, and depression, as well as disruptions in circadian rhythms and environmental factors.
- What strategies and interventions can improve sleep in individuals with ASD? Establishing a consistent sleep routine, addressing sensory sensitivities, and considering the use of melatonin supplements are some of the strategies and interventions that can improve sleep in individuals with ASD [2].
- Why is it important to establish a consistent sleep routine for individuals with ASD? Establishing a consistent sleep routine is important for individuals with ASD as it helps regulate their circadian rhythms and improve overall sleep quality, contributing to their overall well-being.
- How do sensory sensitivities contribute to sleep difficulties in individuals with ASD? Sensory sensitivities can contribute to sleep difficulties in individuals with ASD, and addressing these sensitivities can help improve their sleep quality.
- What are some sleep hygiene tips for individuals with ASD? Sleep hygiene tips for individuals with ASD include maintaining a consistent bedtime, creating a quiet sleeping environment, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and large meals before bedtime, all of which can significantly contribute to better sleep quality.
- What are the effects of disrupted sleep on autism features such as social skills and repetitive behaviours? Disrupted sleep can exacerbate core features of autism, such as poor social skills, more severe repetitive behaviours, and lower intelligence test scores, emphasizing the importance of addressing sleep problems for individuals with ASD.
- How can establishing a routine and using melatonin supplements help people with autism sleep better? Establishing a routine and using melatonin supplements can help regulate circadian rhythms and improve overall sleep quality for individuals with autism, contributing to their overall well-being [2].
- What methods do researchers use to assess sleep problems in people with autism? Researchers use methods such as actigraphy and polysomnography to assess sleep problems in people with autism, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of their sleep patterns and difficulties.
- What treatment options are available for sleep problems in people with autism? Treatment options for sleep problems in people with autism include implementing sleep hygiene practices, addressing co-occurring medical conditions, and considering non-pharmacological interventions and over-the-counter treatments, tailored to the specific needs of individuals with ASD.
This article explores the connection between ADHD and sleep, discussing the impact of sleep disorders on individuals with ADHD, common sleep disturbances, the ADHD effects of sleep duration, treatment options for sleep problems, ongoing research, and frequently asked questions.
Understanding the Link Between ADHD and Sleep
The relationship between ADHD and sleep disorders is complex and multifaceted, with ADHD often having an effect on sleep. Lack of sleep can have a profound impact on individuals with ADHD, leading to a range of physical illnesses, behavioral issues, and mood changes. For example, insufficient sleep can contribute to increased irritability, difficulty concentrating, and impulsivity, all of which are core symptoms of ADHD. Furthermore, sleep deprivation can exacerbate the symptoms of ADHD, making it more challenging for individuals to manage their condition effectively.
In addition to the intrinsic challenges of ADHD, individuals with this condition often face disruptions in their sleep patterns due to circadian rhythm disorders, frequent consumption of caffeinated beverages, the use of ADHD medications, and alcohol consumption, all of which can interfere with their ability to achieve restful sleep. For instance, the stimulating effects of caffeine can make it difficult for individuals with ADHD to fall asleep, while alcohol can disrupt the continuity of their sleep, leading to fragmented rest. These factors collectively contribute to the high prevalence of sleep disturbances in individuals with ADHD.
Moreover, comorbid conditions such as anxiety, depression, and Restless Legs Syndrome can further complicate the sleep experiences of individuals with ADHD. For instance, Restless Legs Syndrome can cause uncomfortable sensations in the legs, leading to difficulty falling asleep and disrupted sleep throughout the night, exacerbating the ADHD effect on existing sleep challenges. Therefore, the interplay between ADHD and various sleep disorders and disturbances underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to addressing the sleep needs of individuals with ADHD.

Common Sleep Disorders Associated with ADHD
Electronic devices, such as smartphones and video games, have been identified as significant contributors to the challenges individuals with ADHD face when trying to fall asleep. The stimulating nature of these devices, combined with the exposure to blue light, can disrupt the natural wind-down process, leading to delayed sleep onset and disrupted sleep patterns. For instance, the engaging content on smartphones or the excitement of video games can keep individuals mentally alert and make it harder for them to transition into a state of relaxation conducive to falling asleep.
Moreover, the prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea and Restless Legs Syndrome in individuals with ADHD further exacerbates their struggles with obtaining restful sleep. Obstructive sleep apnea, characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep due to airway obstruction, can lead to fragmented sleep and daytime sleepiness. Similarly, Restless Legs Syndrome, marked by uncomfortable sensations in the legs and an uncontrollable urge to move them, can disrupt sleep onset and maintenance, affecting the overall quality of sleep experienced by individuals with ADHD.
This underscores the intricate interplay between sleep and ADHD symptoms, as addressing sleep-related issues can have a positive impact on the overall well-being and functioning of individuals with ADHD. Understanding the multifaceted ADHD effects on sleep is crucial in developing comprehensive strategies to address this issue.
Sleep Disturbances
Adults with ADHD not only have trouble falling asleep but also experience frequent awakenings during the night, leading to disrupted and poor-quality sleep. The ADHD effects on sleep can have significant implications for the overall health and functioning of individuals with ADHD, as the impact of sleep disturbances on their daily lives and cognitive abilities can be profound.
For instance, poor sleep quality and duration have been associated with increased levels of daytime sleepiness, which can exacerbate the existing symptoms of ADHD, such as inattention and hyperactivity, consequently leading to a decline in overall daytime functioning. By recognising and addressing sleep disturbances in individuals with ADHD, healthcare providers can play a crucial role in improving their quality of life and overall functioning.
Studies on the ADHD effects on sleep have revealed that adults struggle to fall asleep easily, experience restless sleep, and have difficulty waking up feeling refreshed. Inadequate sleep can contribute to difficulties in sustaining attention, regulating emotions, and managing impulsive behaviors, all of which are core symptoms of ADHD.

Treatment Options for ADHD-related Sleep Problems
When it comes to addressing ADHD effects on sleep, there are various treatment options available to help manage these issues and improve the overall quality of sleep for individuals with ADHD. One common approach involves the use of stimulant-class medications, which can aid in regulating sleep patterns and promoting better rest. For instance, these medications can help individuals with ADHD fall asleep more easily and stay asleep throughout the night, ultimately contributing to improved sleep quality and duration.
In addition to stimulant-class medications, alternative options such as Benadryl, melatonin, and certain antidepressant medications have also been considered as part of the treatment plan for ADHD-related sleep problems. These medications can play a role in addressing specific aspects of sleep disturbances, such as difficulty falling asleep or maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, thereby enhancing the overall sleep experience for individuals with ADHD. For example, melatonin supplements have been found to be particularly effective in regulating the sleep-wake cycle in individuals with ADHD, contributing to more restful and rejuvenating sleep.
Implementing practical interventions for problems waking up can significantly impact the overall sleep quality for individuals with ADHD. For instance, using a two-alarm system or integrating sunset/sunrise-simulating lights into the sleep environment can help individuals wake up more easily and feel more refreshed. These interventions can be valuable in addressing specific challenges related to waking up, which are commonly experienced by individuals with ADHD, ultimately contributing to a more positive and restorative sleep experience. ADHD coaching can also benefit individuals with sleep-related issues, through the personalised strategies that best suit the individual. Therefore, it is important to consider a multifaceted approach to treatment that encompasses both medication-based interventions and practical strategies to address the complex nature of sleep disturbances in individuals with ADHD.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the common sleep disorders associated with ADHD in both children and adults? In individuals with ADHD, common sleep disorders include obstructive sleep apnea, Restless Legs Syndrome, and difficulties in falling asleep and staying asleep, which are often exacerbated by the use of electronic devices and other factors.
- How does lack of sleep affect individuals with ADHD in terms of physical illness, behavioural issues, and mood changes? Lack of sleep can lead to various physical illnesses, behavioural issues, and mood changes in individuals with ADHD, further exacerbating their existing symptoms and impacting their overall well-being.
- What are the effects of caffeine, ADHD medications, and alcohol on the sleep of individuals with ADHD? Caffeine, ADHD medications, and alcohol can interfere with the sleep patterns of individuals with ADHD, contributing to disrupted sleep and challenges in obtaining restful sleep.
- How do other conditions like anxiety, depression, and Restless Legs Syndrome impact the sleep of individuals with ADHD? Comorbid conditions such as anxiety, depression, and Restless Legs Syndrome can significantly impact the quality of sleep in individuals with ADHD, further complicating their sleep patterns and overall well-being.
- What role do electronics, such as smartphones and video games, play in affecting the ability of individuals with ADHD to fall asleep? Electronics, such as smartphones and video games, can impact the ability of individuals with ADHD to fall asleep, often leading to delayed sleep onset and disrupted sleep patterns.
- Can removing tonsils improve symptoms in children with ADHD and sleep-related breathing disorders? Yes, in some cases, the removal of tonsils has been found to alleviate symptoms in children with ADHD and sleep-related breathing disorders, highlighting the complex relationship between sleep and ADHD symptoms.
- What are the most common ADHD effect on sleep disturbances experienced by adults? Adults with ADHD commonly experience difficulties in falling asleep, restless sleep, and challenges in waking up feeling refreshed, all of which can significantly impact their daily functioning and well-being.
- What treatment options are available for ADHD-related sleep problems? Treatment options for ADHD-related sleep problems encompass a range of approaches, including the use of medications, behavioral interventions, and environmental modifications to improve sleep quality in individuals with ADHD.
- How does sleep duration impact the daytime functioning of children with ADHD? Shortened sleep duration is causally linked to poorer daytime functioning in children with ADHD, emphasizing the critical role of adequate sleep in managing their symptoms and overall well-being.
- What are the associations between sleep problems and risky driving, less physical activity, and other health behaviors in individuals with ADHD? Sleep problems in individuals with ADHD are associated with risky driving, less physical activity, and other health behaviors, highlighting the importance of addressing sleep disturbances as part of comprehensive ADHD management and care.